Development of a New Design for a Spaceborn Telescope
Investigation and design of a new telescope for space applications.
Description
The Aim in this project is to investigate and design a new telescope system for space applications. The goal is to design a 30 cm diameter off-axis system with a focal length of 2 meters covering a wavelength range from 550 nm to 2700 nm. The mass is a serious constraint and approaches to reducing mass are part of the project. The work is in conjunction with Swiss industry (Thales-Alenia Space Switzerland) and should result in a preliminary design for one or more potential applications.
Abstract
Present and past satellite-based telescopes cover a wide range of optical observation properties. The size, design and features of a telescope varies greatly depending on the observed target. Capabilities include broad ranges in wavelength, great details in image resolution, stereo imaging and many more. Future optical observation systems aim to improve upon the capabilities of past systems as new targets of interest are discovered.
The goal of this project is to create a preliminary design for a new telescope system for space application. This entails the theoretical analyses and simulations of an optical model, a search for materials suitable for optical space applications and finally a preliminary design and simulations of components and the telescope structure.
The dedicated area of application implies an extremely detailed analysis of each feature of a system. Therefore, a complete flyable final design and model lies beyond the scope of a CE-lab. The goal is to create a preliminary design with a basic simulation and analysis from which a final design can be derived and optimized.
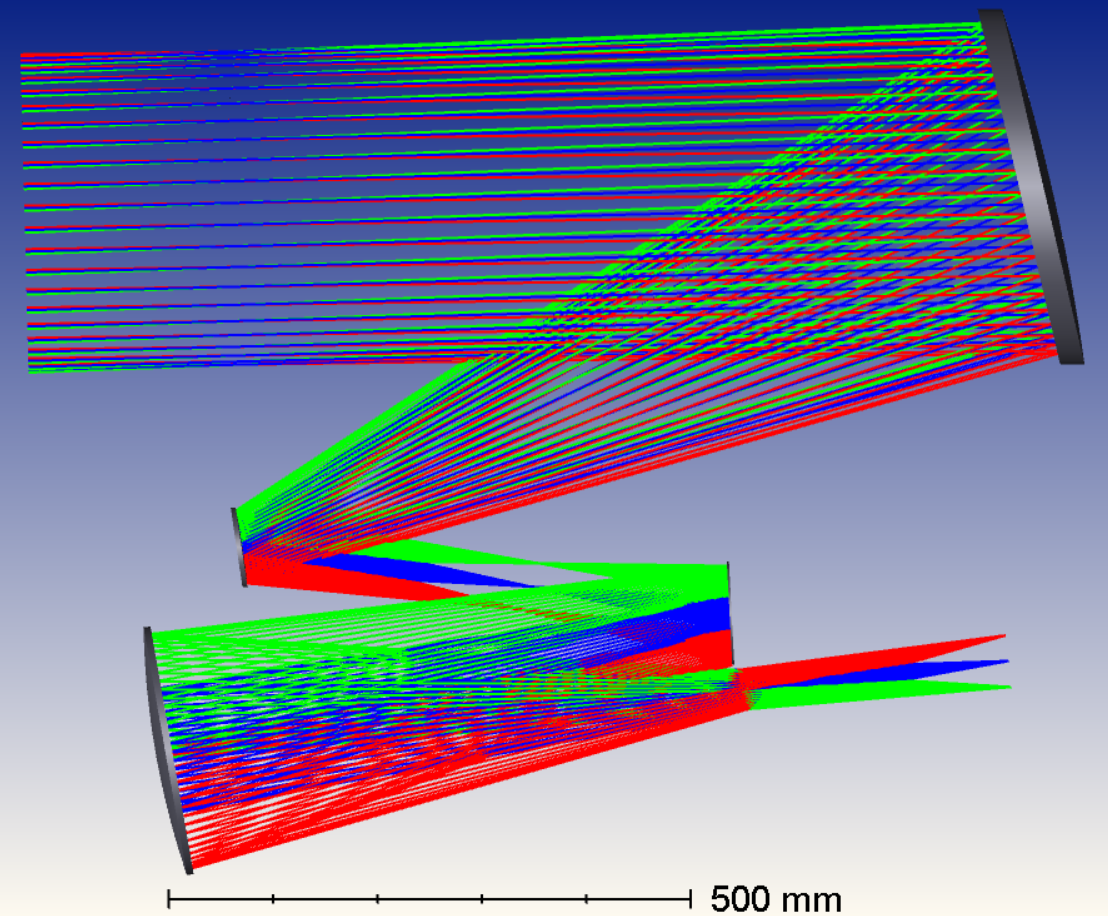
The telescope design is a 30cm diameter, 4 mirror off-axis system with a system focal length of approximately 2 meters. The curvatures and shapes of the off-axis, aspheric mirrors are designed to correct any 3rd order aberration in the projected image within a broad range of wavelengths. Straylight baffles and additional apertures are intended in the design to improve the image quality.
An optical raytracing simulation confirms the absence of aberrations in the produced image as well as the correct focal length and focal spot sizes. From this model, the mirror dimensions and exact shapes are derived into a mechanical model, which is then used for lightweighting the mirror substrates and designing the mirror mounts and telescope structure. The different designed components are used in several FE-models, analysing the stiffness (Eigenfrequency), thermoelasticity, isostaticity and manufacturability.
Impressions
Contact
- Name / Titel
- Prof. Nicolas Thomas
